Harness AI for Faster, Smarter Web Searches: Time-Saving Tips & Tools
Translators and interpreters search the web dozens of times every day. And the search engine you use makes a huge difference.
In this article, we explore how browsers and search engines work together, dive into advanced search features in Google and Bing, and show you how to harness AI for faster, more precise results.
Browsers and search engines: Same thing?
Although it’s easy to mix them up, browsers and search engines are not the same thing.
A browser is an app for accessing websites, while a search engine is a website that helps you find information online. Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Safari are browsers. Google, Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo are search engines.
The confusing part? Opening a browser usually takes us to its default search engine. For example, Chrome opens to Google, and Edge opens to Bing.
But you don’t have to stick with your browser’s default search engine – or even your default browser! You can use Chrome to search on Bing, or Edge to search on Google. And you can set any search engine as your default.
Pro Tip: Start a search in any browser by typing your query directly in the address bar.
Why experiment with browsers and search engines
Browsers differ in speed, resource use, and privacy settings, while search engines not only deliver different results but display them in unique ways.
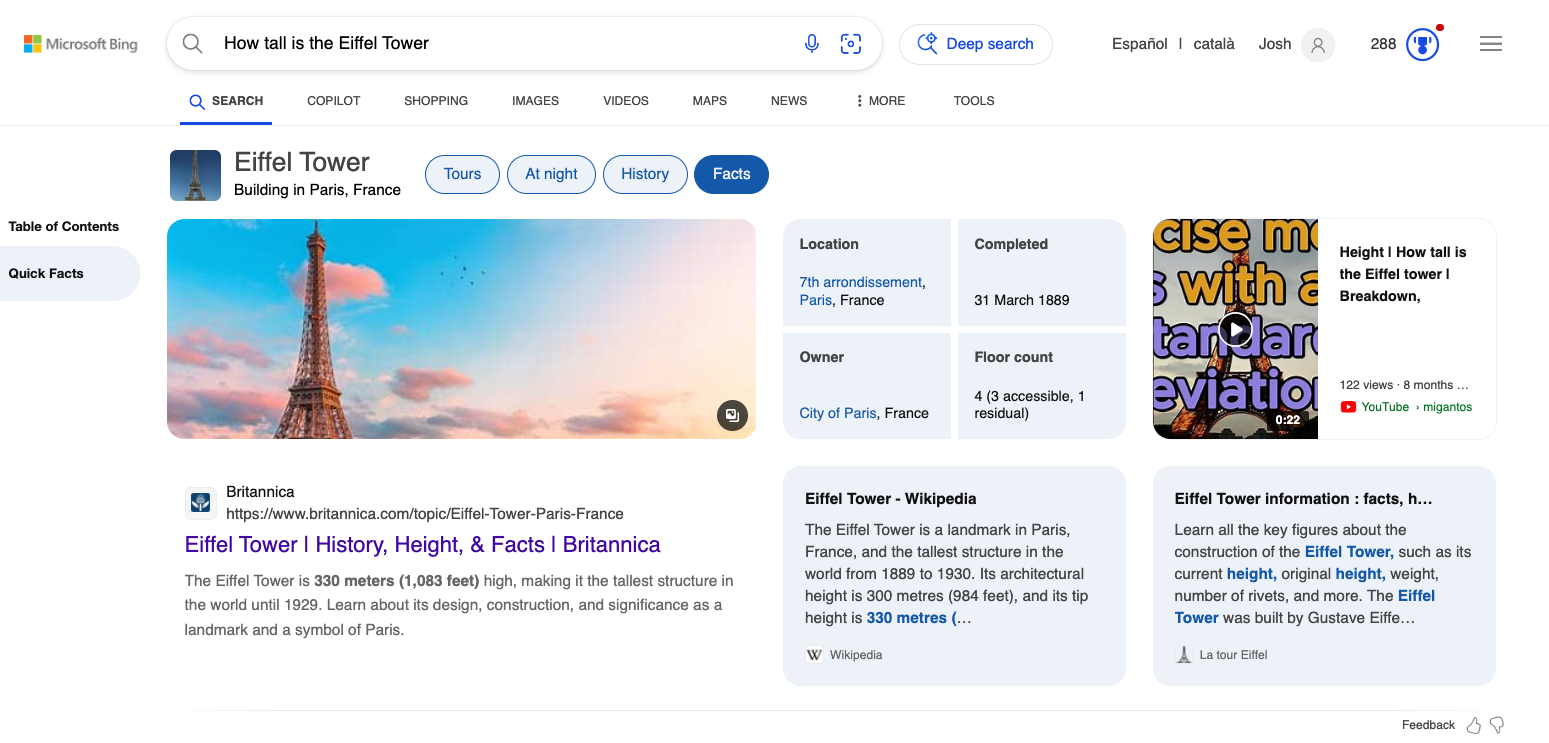
Google search results on Chrome
Bing search results on Microsoft Edge
Both browsers and search engines get frequent updates – whether for performance improvements, security enhancements, or new functionalities – but they don’t all evolve at the same pace.
Exploring different browsers and search engines, or trying a setup different from your default, can help you unlock the best tools to enhance your workflow.
Note: Search engine features may vary by browser. For example, some Bing features in Edge aren’t accessible in Chrome. Location also affects which features you see, and even the appearance of search engine homepages.
Refine search engine results with advanced search operators
No matter which browser or search engine you use, advanced search operators help you filter results and get the facts you need faster. Here are a few you’ll want to know:
Use quotation marks (“ ”) to search exact phrases (for example, “solar system”) and the minus sign (-) to exclude terms (for example, “solar system” -earth to exclude Earth).
Try site-specific searches to get results from specific websites. Type site:followed by the website address and keywords (for example, site: nasa.gov venus temperature).
To filter for PDFs, PowerPoints, or other formats, search by file type. Type filetype:followed by the file type and your keywords (for example: filetype: PDF solar system).
Run a wildcard search if you can’t remember the exact wording of a phrase or want to find common word pairings. Type the phrase in quotation marks and use an asterisk (*) as a placeholder for the missing word (for example, “The * day on record”).
Maximize Google search with key tools and features
You’re likely familiar with Google’s basic search filters – the buttons under the search box that let you switch between images, videos, news, and more.
When you search for a well-known company or celebrity, Google opens a knowledge panel on the right with additional filters that allow you to dive into specific details like albums, movies, or awards. (Bing takes this a step further – more on that below!)
Google’s knowledge panel lets you quickly access additional information
The Tools menu offers more options to optimize your searches.
After launching a search, click Tools to open the Tools menu.
Select Any time to filter results by timeframe, such as the past hour, 24 hours, or week. This is especially useful for discovering recent developments related to your assignment.
Use All results > Verbatim to limit results to exactly what you typed. This helps when searching for exact phrases, names or brands with unique spelling – otherwise, Google search will automatically “correct” your search.
To further customize your search, click Advanced Search to refine results by language, region, last update, file type, and more – the ideal way to narrow hits to your target language.
Advanced search settings on Google
Want to check how common a term or expression is? Clicking Tools reveals the number of results on the right-hand side of your screen.
Discover Bing’s AI-powered search tools
Like Google, Bing lets you narrow results by images, videos, news, shopping, and more.
But as I mentioned earlier, Bing takes search refinement one step further. It offers search-specific filters for a broader range of queries – not just celebrities or well-known companies. For example, a search for “solar system planet distances” produces content categories like Planets, Stars, Magnitude, Luminosity, and more.
Bing’s AI-powered search-specific filters
Typing a question in Bing’s search box generates additional questions and related searches, as shown below. Bing’s enhanced search bar may even display an AI chatbox with suggested prompts.
Bing’s AI-powered predictive suggestions help users find information faster
Like Google’s featured snippets, Bing provides direct answers to questions with the Answers feature. The difference? Bing’s Answers are generated by AI and include sources, follow-up questions, and an instant chat with the AI assistant, Copilot.
Bing’s search results are also more comprehensive and visually dynamic than Google’s. On the left side of the screen, you’ll find related searches, while on the right side you’ll find knowledge cards with facts, image-based timelines, and more.
Knowledge cards on Bing. Source: Microsoft Bing blogs
If you scroll down Bing's results page, you'll find a 'People also ask' section, along with a selection of images and videos, just like on Google.
Even better, Bing highlights additional content types based on your query, like PDFs. Bing’s videos also have autoplay previews, which Google doesn’t currently offer.
Another exciting Bing feature is deep search, which uses AI to understand the search intent behind the keywords you typed. If the intent is unclear, Bing will ask for clarification – for example, if your search for “solar system” is for astronomy research or solar system education. Deep search results are also more comprehensive, which makes them ideal for complex queries.
Blending Google and Bing
Faithful to Google, but curious about Bing? With Edge, you can see Google and Bing results side by side. Start a search on Google, select any word from a result, and a side panel will pop up with related Bing results.
Prefer sticking with Chrome and Google but want the convenience of Copilot right on your search screen? Download the Copilot (Bing Chat) in Google extension to integrate AI into your searches.
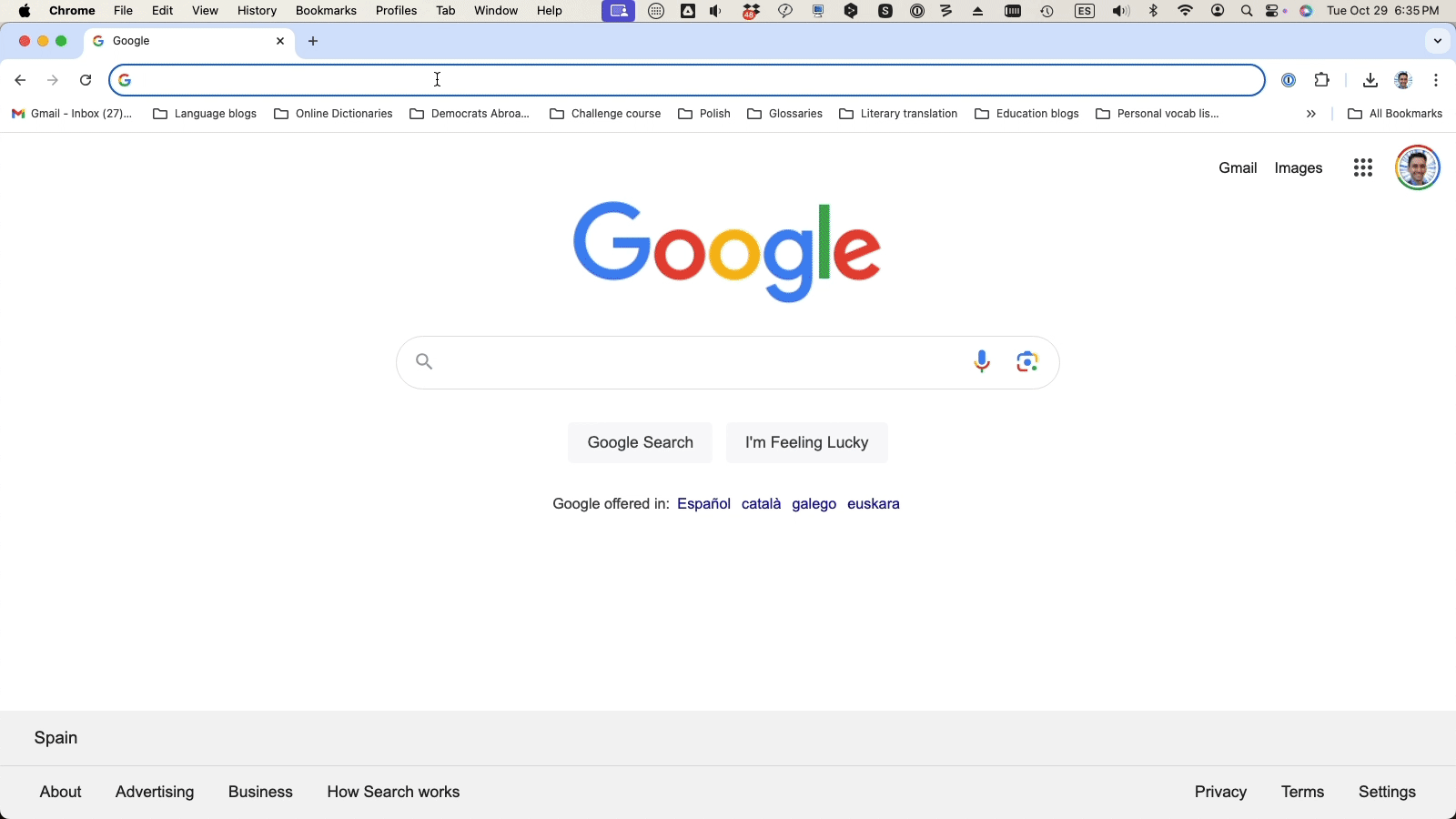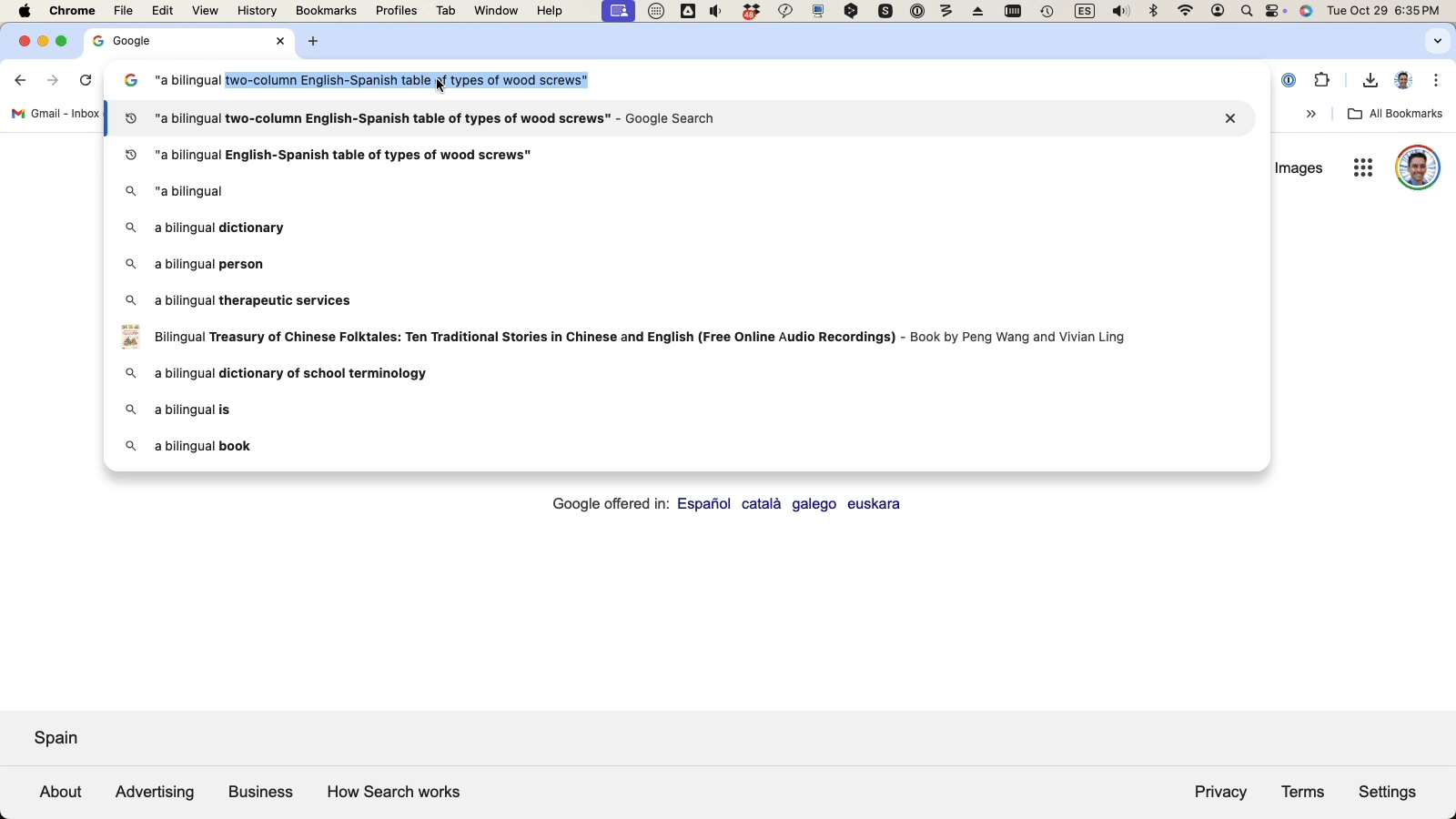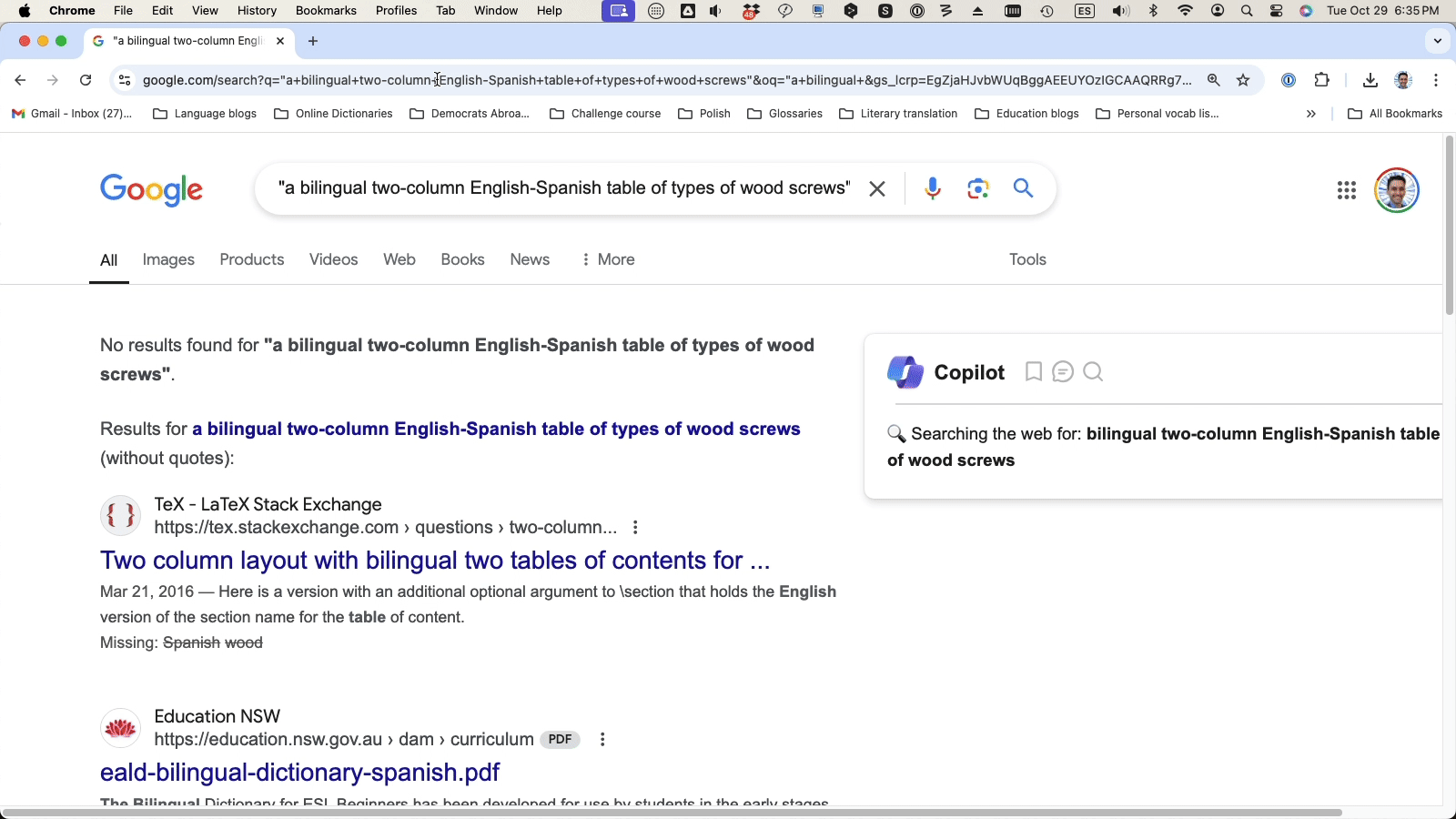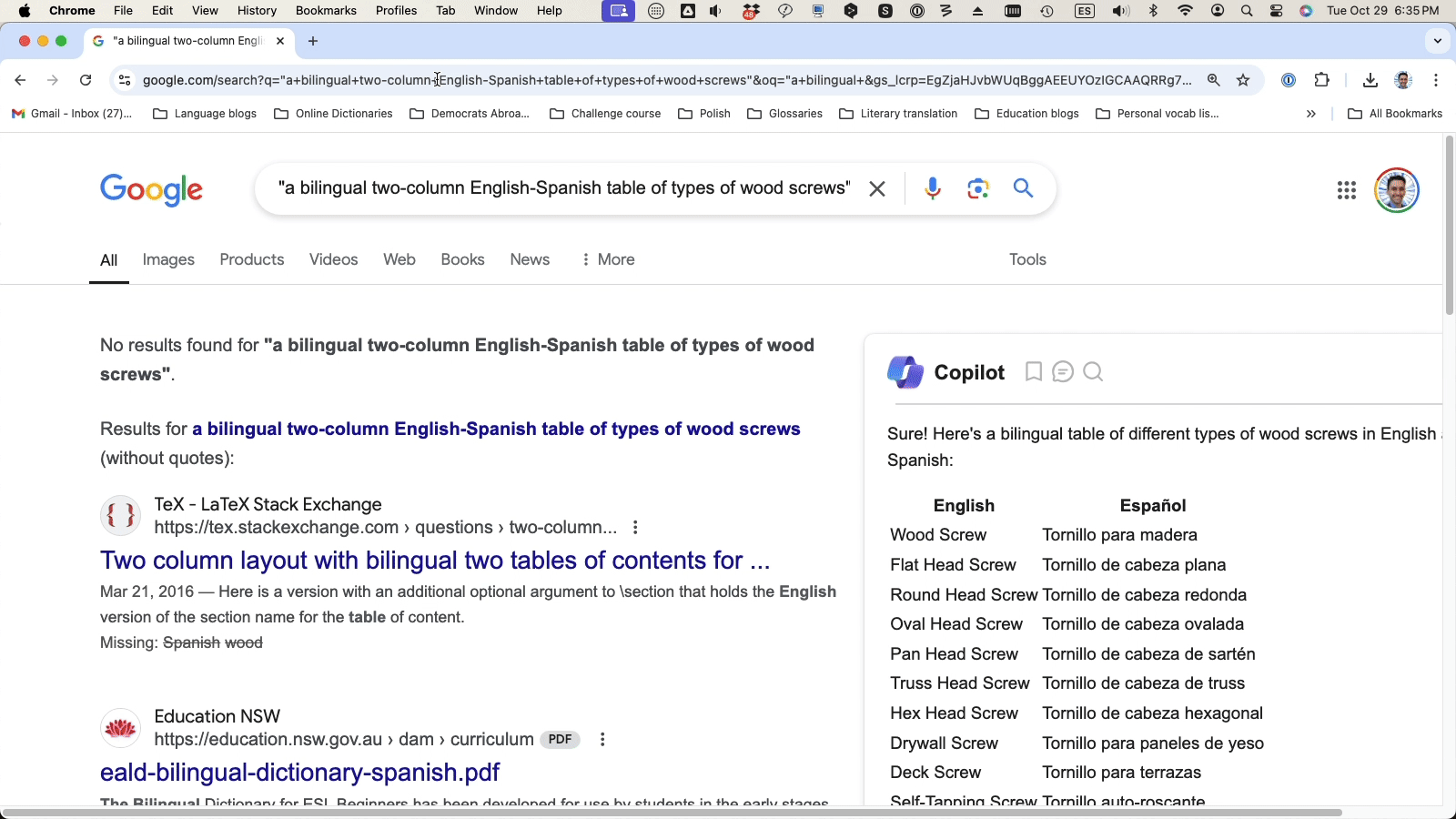
Then, run a hybrid search – a combination of a keyword query with an AI prompt – for more effective results.
Keyword query: “types of wood screws”
AI prompt: “give me a bilingual English-Spanish table of types of wood screws”
Hybrid search: “a bilingual English-Spanish table of types of wood screws”
(The hybrid search is your best bet for getting a structured table that neatly organizes the terms into columns by language.)
Hybrid search combining AI-powered tools with traditional search methods
Take your search to the next level
Whether you’re in the booth hunting down the titles of a speaker’s published books or at home scrambling to find the equivalent of a hex head structural screw before your translation deadline, every minute counts.
Fortunately, the companies behind major browsers and search engines are working hard to enhance efficiency, making it quicker and easier to find and view information than ever before.
So, step out of your comfort zone – discover new features in your go-to search engine or try an alternative search engine or browser.